Fiber vs. DSL: What’s the Difference?
Figuring out which high-speed internet plan to sign up for can be confusing when you’re faced with two different types of internet connection: Fiber and DSL.
When deciding between fiber internet and DSL internet, there are a few key factors to consider. Fiber internet is generally considered to be faster and more reliable than DSL internet, as well as being able to support larger amounts of data and faster upload/download speeds.
It’s important to consider the specific needs, budget, and availability in your area, as well as the desired speed and reliability.
However, fiber internet may not be available in all areas, and it may also be more expensive than DSL internet. DSL, on the other hand, uses existing telephone lines to connect to the internet and more widely available and generally less expensive than fiber internet, but may also be subject to slower speeds and less reliable connections, especially during high traffic periods.
What is DSL Internet?
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) internet is a type of broadband internet connection that uses existing copper telephone lines to provide high-speed internet access. Unlike traditional dial-up internet, there is no need to tie up the phone line while browsing, as data is carried over a separate frequency band.
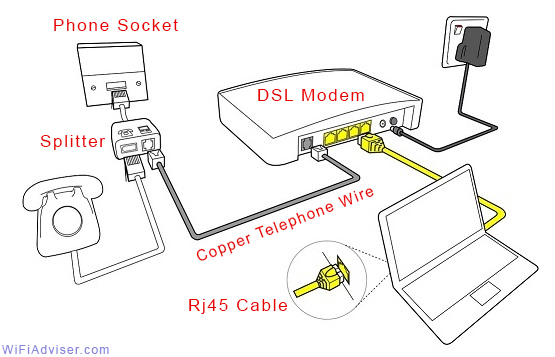
Demystifying DSL Internet: Unveiling the Connection Topology
DSL connections can be asymmetrical or symmetrical, meaning that the download and upload speeds are different or the same respectively. Asymmetrical connections are typically used for residential purposes, where users require faster download speeds for activities such as streaming and gaming. Symmetrical connections are more commonly used in businesses, where uploading large amounts of data is also required.
DSL internet speeds can vary depending on your distance from the provider.
DSL internet has been around for over 20 years and is still widely used today, particularly in areas where access to fiber-optic or cable internet is limited. While it’s speeds may not be as fast as some other types of broadband internet, it can still provide a reliable and affordable option for many internet users.
What is Fiber Internet?
Fiber internet is the latest and fastest type of broadband internet connection using optical fibers to transmit data signals over long distances. It is an upgrade from traditional copper wire connections, providing faster speeds and more reliable connections. You may hear terms like FTTX ,FTTH, GPON , … for fiber internet technology.
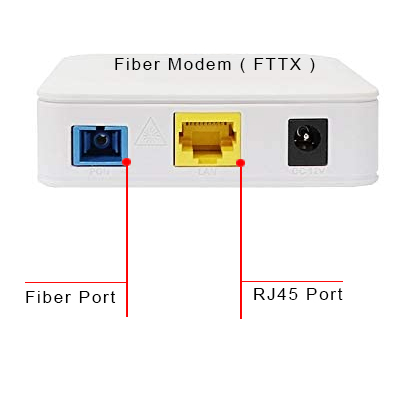

Delving into GPON ONT Technology: Exploring Ports and Purpose
Fiber optic cables are made of thin glass or plastic fibers that transmit data signals using light, which allows the signals to travel at a faster speed and over longer distances without losing signal strength. This technology offers bandwidth speeds of up to one gigabit per second, which is 100 times faster than traditional copper wire connections.
Fiber optic cables are less susceptible to interference and corrosion compared to traditional copper cables used for DSL connections. So it is much more reliable and stable than DSL internet.
As a result, fiber internet is becoming increasingly popular as more people require faster internet speeds for streaming services, online gaming, and remote working. It is also more secure and durable than traditional copper wire connections. Its cost may be higher than traditional connections, but the advantages it offers make it a top choice for many users.
Fiber vs. DSL: Technical Differences at a Glance
Technology: Fiber optic internet uses thin, flexible strands of glass or plastic cables that transmit data using light. On the other hand, DSL internet uses telephone lines to transmit data through copper wires.
Speed: Fiber optic internet offers faster speeds compared to DSL. Fiber can provide symmetrical speeds (same upload and download speeds) of up to 10 Gbps, while DSL typically offers download speeds ranging from 1-100 Mbps and upload speeds of 1-10 Mbps.
Bandwidth: Fiber internet offers higher bandwidth capacities, allowing for multiple devices to connect simultaneously without experiencing significant slowdowns. DSL has limited bandwidth, which can result in slower speeds when multiple devices are connected.
Distance: DSL internet connectivity can be affected by distance from the provider’s central office. As the distance increases, the signal strength weakens, and the speed decreases. Fiber optic internet has negligible signal degradation regardless of the distance between the user and the provider.
Reliability: Fiber optic internet is more reliable as it is less prone to interference from factors like weather conditions or electrical interference. DSL internet can be affected by factors like distance, quality of wiring, and nearby electrical devices.
Availability: DSL is widely available as it utilizes the existing telephone infrastructure. Fiber optic internet, however, may not be readily available in all areas, as it requires the installation of new fiber-optic cables.
Cost: DSL internet tends to be cheaper than fiber optic internet. Fiber connections require significant infrastructure investments, while DSL connections can utilize existing copper telephone lines.





