Internet Speed Test Result
When interpreting the results of Internet speed tests, there are three main metrics to consider: download speed, upload speed, and ping Time (or latency). The download speed measures the rate at which data can be downloaded from the Internet to your device, whereas the upload speed measures the rate at which data can be uploaded from your device to the Internet. The ping measures the time it takes to establish a connection with a server and receive a response.
Demystifying the Key Metrics: Download, Upload, and Ping Time
Every internet speed test typically measures three key metrics: download speed, upload speed, and ping rate. These metrics provide insights into different aspects of your internet connection.
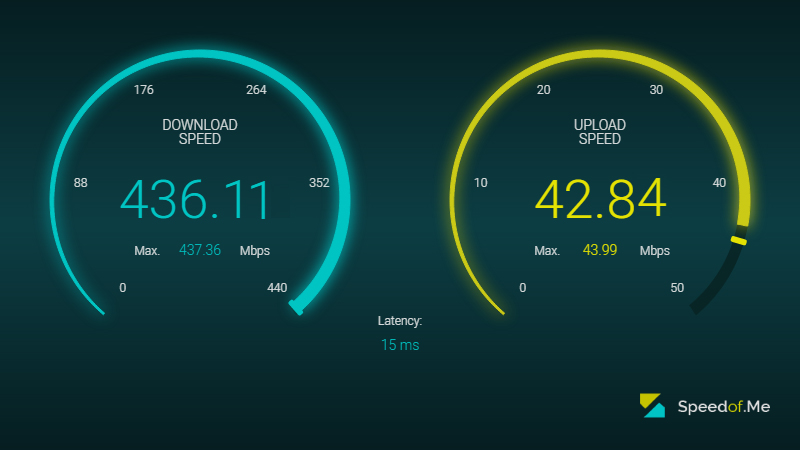
Decoding Internet Speed Test Results: Download , Upload and Latency (Ping Time)
Download speed
This metric indicates the rate at which data is downloaded from the internet to your device. Higher download speeds enable faster streaming of videos, downloading of large files, and smooth online gaming.
Upload Speed
This metric indicates the rate at which data is uploaded from your device to the internet. Upload speeds are crucial for tasks like video conferencing, file sharing, and cloud storage.
Ping Time (Latency)
Also known as latency, ping rate measures the round-trip time it takes for a data packet to travel from your device to the internet server and back. Lower ping rates imply faster response times and smoother online interactions.
Read More : What is Streaming ?
Understanding the Baseline
Your internet service provider (ISP) typically advertises the maximum download and upload speeds you can expect with your internet plan. These advertised speeds represent the theoretical maximum speeds under ideal conditions, and your actual speeds may vary due to factors like network congestion, distance from the ISP’s network, and the number of devices connected to your network.
Contextualizing Your Results
Your device’s capabilities also play a role in determining actual internet speeds. Devices with older Wi-Fi adapters or slower processor speeds may not be able to fully utilize the available bandwidth, resulting in slower speeds even with a high-speed internet connection.
Additionally, network usage patterns can significantly impact your internet performance. During peak hours or when multiple devices are simultaneously using the internet, network congestion can occur, leading to reduced speeds for all users.
To obtain a more accurate assessment of your internet speeds, it’s recommended to conduct tests at different times of the day and on different devices.
Interpreting Outliers
If your test results consistently fall below the advertised speeds or expectations, it’s worth investigating potential bottlenecks in your network. Router placement, interference from neighboring networks, and outdated router firmware can all contribute to slower speeds. By identifying these potential issues and implementing optimization strategies, you can often significantly improve your internet performance.
What Speed (Bandwidth) Do I Really Need?
Based on the www.Broadbandnow.com recommendations, you need:
- Check email and browse the web: 1-5 Mbps minimum
- Stream HD content: 15-25 Mbps minimum
- Stream 4K content and play competitive online games: 40-100 Mbps minimum
- Stream 4K content, play online games, and download very large files: 200+ Mbps minimum
Most households need internet speeds of at least 100 Mbps to enjoy activities like streaming video on multiple devices. You can use Bandwidth Calculation Tool to calculate the required internet speed based on the number of users and devices in your home.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with Informed Decisions
Understanding and interpreting internet speed test results is an essential step in ensuring you’re getting the most out of your internet connection. By understanding the key metrics, comparing your results to your ISP’s advertised speeds, and considering contextual factors, you can make informed decisions about optimizing your network and enjoying seamless online experiences.






