WiFi6 Technical Specifications
With the ever-increasing demand for faster and more reliable internet, the advent of WiFi6 technology has brought forth a significant improvement in wireless connectivity. WiFi6, also known as 802.11ax, boasts revolutionary technical specifications that make it the ideal wireless solution for both home and business environments.
WiFi 6 is the successor to the WiFi 5 (802.11ac) standard and operates in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz spectrums. This standard enables devices ( WiFi Routers / Clients ) to send more data in one transmission stream, resulting in speed improvements of up to 20% to 40% with higher modulation rate (1024-QAM). Higher modulation increases the efficiency and speed of data transmission on your network.
WiFi6 Technical Overview
One of the significant improvements of WiFi6 is the introduction of Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) technology. OFDMA enables multiple devices to receive and transmit data simultaneously, thereby reducing network congestion. This breakthrough technology also helps to enhance battery life for devices with lower power requirements.
WiFi6 also offers higher throughput rates of up to 9.6 Gbps, which is about three times faster than its predecessor, WiFi5. This high throughput rate is achieved through the use of 1024-QAM modulation, allowing for more significant data transmission speeds.
Frequency Bands and Channels
WiFi6 operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, providing a wider range of options for network deployment and device compatibility. The 2.4 GHz band offers wider coverage and better compatibility with legacy devices, while the 5 GHz band provides higher data rates and reduced interference.
The 2.4Ghz band is available in WiFi6 standard, while the industry has shifted to 5Ghz WiFi for less interference. 2.4Ghz is still better at penetrating solid objects. And there shouldn’t be as much interference for 2.4Ghz as old wireless (non-WiFi but 2.4Ghz) equipment like cordless telephones and wireless baby monitors are retired.
WiFi Standards Technical Overview
WiFi6 Architecture Enhancements
Very important optimizations have been made in the Wi-Fi 6 architecture, which has increased the speed and quality of communication by 40%. These are as follow:
Number of Spatial Streams
There is one Spatial Stream for each WiFi Router’s antenna, if your router has 4 antennas , you have 4 spatial streams . Technically, the spatial streams can be used to increase the throughput or to increase the quality.
| 802.11 Standard | Maximum Number of Spatial Streams |
| 802.11n | 4 |
| 802.11ac | 8 |
| 802.11ax | 8 |
Symbol and guard intervals(GI)
- Symbol is the transmission signal in the time domain.
| Before 802.11ac | 802.11ax |
| 3.2 us | 12.8 us |
- Guard Interval (GI) is a gap between two adjacent symbols to avoid interference with each other.
| Before 802.11ac | 802.11ax |
| 0.8 us 0.4 us (Short GI) | 0.8 us 1.6us (2*GI) 3.2 us (4*GI) |
Encoding Scheme
The encoding scheme is the modulation technology, Means the number of bits that can be carried in a symbol.
| 802.11 Standard | Higher-Order Modulation | Number of Bits in a Symbol |
| 802.11n | 64-QAM | 6 |
| 802.11ac | 256-QAM | 8 |
| 802.11ax | 1024-QAM | 10 |
Number of valid subcarriers
Carriers are similar to symbols but in the frequency domain. One subcarrier carries one symbol, and the number of subcarriers varies according to the modulation mode and frequency bandwidth.
Number of Subcarriers in each channel width and standard :
| Channel Width | 802.11n | 802.11ac | 802.11ax |
| 20Mhz | 52 | 234 | 242 |
| 40Mhz | 108 | 468 | 484 |
| 80Mhz | 234 | 980 | 996 |
| 160Mhz | 2 x 234 | 2 x 980 | 2 x 996 |
In conclusion , maximum data rate of 802.11ac standard is 433Mbps and maximum data rate of 802.11ax is 600Mbps, with 1 Spatial Stream at HT80.
Read More : Where to Place WiFi Router? and What is WiFi Channel and Channel-Width?
WiFi 6 Technology Features
Channel Width and OFDMA
WiFi 6 supports channel widths of up to 160 MHz, allowing for greater bandwidth and faster data transfer rates. It also includes a feature called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), which divides each channel into smaller sub-channels, allowing multiple devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously.
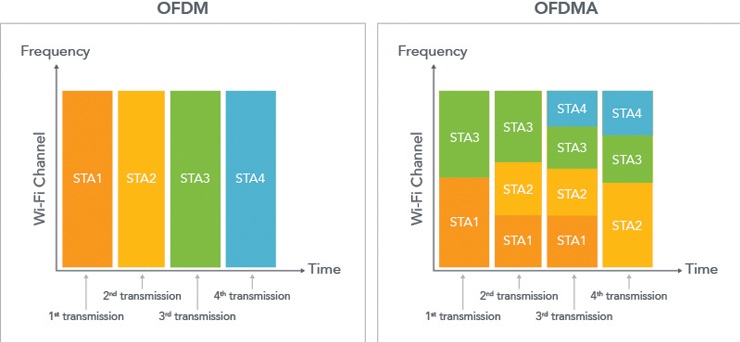
WiFi6 Specifications
MU-MIMO Technology
WiFi 6 employs both Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO) and Single-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (SU-MIMO) technologies. MU-MIMO enables multiple devices to transmit and receive data simultaneously, while SU-MIMO allows a single device to utilize multiple antennas for better signal quality and coverage.
Frequency Bands
WiFi 6 operates in both the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands, just like its predecessors (WiFi 5, WiFi 4). However, it introduces additional frequency bands for better performance, including 1.2 GHz, 6 GHz, and 60 GHz.
Data Rates
WiFi 6 offers significantly higher data rates compared to previous generations. It can achieve peak data rates of up to 9.6 Gbps (gigabits per second) by utilizing multiple streams and wider channel widths.
Target Wake Time (TWT)
TWT is a new feature introduced in WiFi 6 that allows devices to negotiate and schedule their power-saving periods. This helps reduce energy consumption and extends battery life, especially for devices such as IoT sensors and smart devices.
BSS Coloring
BSS coloring enables devices operating in the WiFi6 standard to differentiate between signals from their own network and signals from other networks. This feature increases the efficiency and capacity of your network.
Backward Compatibility
WiFi 6 is designed to be backward compatible with older WiFi standards, ensuring that devices using previous generations (WiFi 5, WiFi 4) can still connect to a WiFi 6 router. However, the full benefits of WiFi 6 can only be realized when both the router and the device support the new standard.
Conclusion
WiFi 6 offers faster speeds, increased capacity, better performance in crowded environments, and improved power efficiency compared to previous WiFi standards. It is expected to provide a more seamless and reliable wireless experience for users across a wide range of devices.





