What is Li-Fi Technology
Wi-Fi is the most common way of connecting to the internet wirelessly, but it is not the only one. There is another wireless technology that promises to be faster, more secure, and more versatile than Wi-Fi. It is called Li-Fi, and it uses light instead of radio waves to transmit data.
In this blog post, we will explain what Li-Fi is, how it works, what are its advantages and disadvantages, and where you can find it.
What is Li-Fi?
Li-Fi is short for Light Fidelity and is a communication system that utilizes light, rather than radio waves, to transmit data. A Li-Fi network uses infrared LED lamps to transmit and receive data by modulating the light intensity at very high speeds, beyond the human eye’s perception.
The term Li-Fi was first coined by Professor Harald Haas in his 2011 TED Global talk, where he demonstrated the concept of using light bulbs as wireless routers. Since then, Haas has co-founded a company called pureLiFi, which develops these products and solutions.

How Does Li-Fi Work?
Li-Fi works by converting data into binary code (a series of ones and zeros) and then encoding it into light pulses. These light pulses are then sent from a transmitter (such as an LED lamp) to a receiver (such as a photodetector or a camera) that can decode them back into data.
However, this technology has a few limitations. It requires a direct line of sight between the light source and the receiving device, as light cannot pass through obstacles like walls. This restricts its range and makes it more suitable for localized applications. Furthermore, sunlight and other strong sources of light can interfere with the data transmission, affecting its reliability.
The transmitter and receiver can communicate in two ways: either in a one-way or a two-way mode.
One Way Mode
In a one-way mode, the transmitter only sends data to the receiver, without receiving any feedback. This is suitable for applications such as broadcasting or streaming.
Two Way Mode
In a two-way mode, the transmitter and receiver can exchange data in both directions, allowing for interactive communication. This is suitable for applications such as internet access or video conferencing.
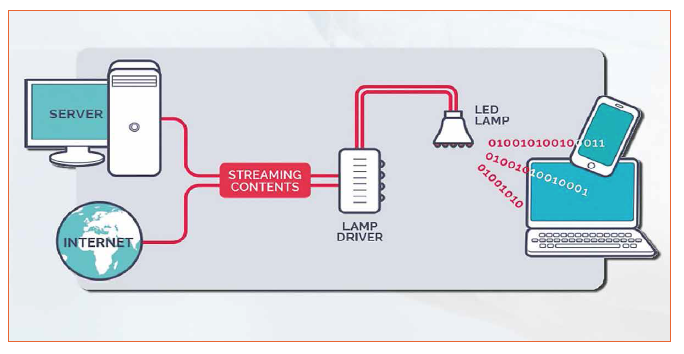
Credit: led-professional.com
Li-Fi Works in Different Frequency Bands
The transmitter and receiver can also communicate in different frequency bands: either in the visible light spectrum, the ultraviolet spectrum, or the infrared spectrum. The visible light spectrum is the range of wavelengths that humans can see, from violet to red. The ultraviolet spectrum is the range of wavelengths that are shorter than violet and invisible to humans. The infrared spectrum is the range of wavelengths that are longer than red and invisible to humans.
Read More: WiFi Channels and Channel Width
The choice of frequency band depends on the application and the environment. For example, visible light can be used for indoor applications where there is no natural light interference, such as in offices or homes. Ultraviolet light can be used for outdoor applications where there is no direct sunlight exposure, such as in tunnels or underground. Infrared light can be used for both indoor and outdoor applications where there is no need for illumination, such as in security or military.
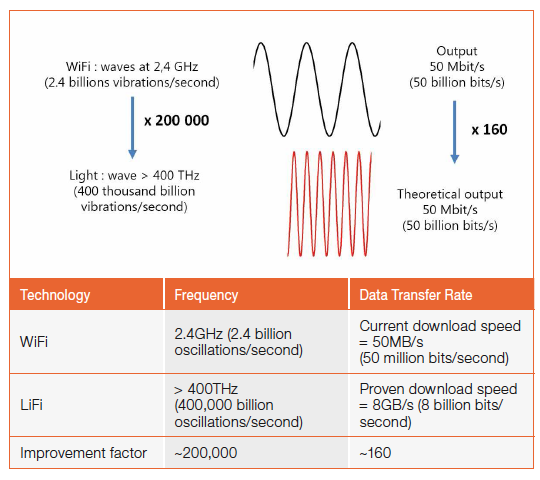
Credit: led-professional.com
What Are The Advantages of Li-Fi?
Li-Fi has several advantages over Wi-Fi, such as:
- Speed: It can achieve data rates up to 224 Gbps, which is much faster than Wi-Fi’s maximum speed of 9.6 Gbps. This is because Li-Fi uses a wider bandwidth of light than Wi-Fi’s limited bandwidth of radio waves.
- Security: It is more secure than Wi-Fi because light cannot penetrate walls or other physical barriers, unlike radio waves. This means that Li-Fi signals are confined to a specific area and cannot be intercepted or hacked by outsiders.
- Capacity: Li-Fi has more capacity than Wi-Fi because there are more available light sources than radio sources in the world. For example, there are billions of LED lamps that can be used as Li-Fi transmitters, compared to millions of Wi-Fi routers.
- Efficiency: It is more energy-efficient than Wi-Fi because it uses existing LED lamps that are already used for lighting purposes, without requiring additional power or infrastructure. Moreover, Li-Fi does not generate any electromagnetic interference or radiation that can harm humans or devices.
- Versatility: Li-Fi can be used in various environments and applications where Wi-Fi cannot operate well or at all. For example, Li-Fi can be used in places where radio waves are prohibited or restricted, such as hospitals, airplanes, or submarines. It can also be used in places where radio waves are congested or unreliable, such as stadiums, malls, or factories.
What Are The Disadvantages of Li-Fi?
Li-Fi also has some disadvantages compared to Wi-Fi, such as:
- Range: Li-Fi has a shorter range than Wi-Fi because light attenuates faster than radio waves over distance. Moreover, Li-Fi signals can be blocked by any opaque object or material that comes between the transmitter and receiver.
- Compatibility: Requires special devices and equipment that are compatible with light communication technology. Most existing devices and networks use radio communication technology and cannot communicate with Li-Fi devices without adapters or converters.
- Availability: Depends on the availability of light sources and receivers in a given area. If there is no light source or receiver nearby, there is no Li-Fi connection. Moreover, Li-Fi may not work well in bright or dark environments, where the light signal may be too weak or too strong to be detected.
Where Can You Find Li-Fi?
Li-Fi is still an emerging technology that is not widely available or adopted yet. However, there are some companies and organizations that are developing and testing products and solutions for various applications and markets. Li-Fi has numerous potential applications, including in hospitals, where it could reduce the risk of electromagnetic interference with medical equipment.
Some examples of applications are:
- Indoor positioning: Can be used to provide accurate and real-time location information for indoor environments, such as museums, airports, or malls. For example, Philips Lighting has developed a Li-Fi system that can guide visitors to their destinations using LED lamps and smartphone cameras.
- Smart lighting: Can be used to create smart lighting systems that can adjust the brightness, color, and mood of the light according to the user’s preferences or activities. For example, Oledcomm has developed a Li-Fi system that can control the light settings of a room using a smartphone app.
- Internet access: Li-Fi can be used to provide high-speed internet access for users who do not have access to Wi-Fi or broadband networks. For example, pureLiFi has developed a system that can connect users to the internet using LED lamps and dongles.
- Education: It can be used to enhance the learning experience for students and teachers by providing interactive and multimedia content through light. For example, Fraunhofer HHI has developed a Li-Fi system that can transmit educational videos and materials from a projector to a tablet.
Conclusion
Li-Fi is a wireless communication technology that uses light to transmit data. It offers several benefits over Wi-Fi, such as speed, security, capacity, efficiency, and versatility. However, it also faces some challenges, such as range, compatibility, availability, and cost.
It is still in its early stages of development and adoption, but it has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate and access information in the future. If you are interested in learning more about Li-Fi or trying it out yourself, you can check out some of the companies and products mentioned in this blog post.





