In today’s wireless-dependent world, having a strong and reliable WiFi connection is essential for seamless connectivity and productivity. Traditional WiFi routers have traditionally struggled to provide consistent coverage throughout large homes or multi-story buildings, leading to dead zones and unreliable connections. This is where mesh WiFi comes into play.
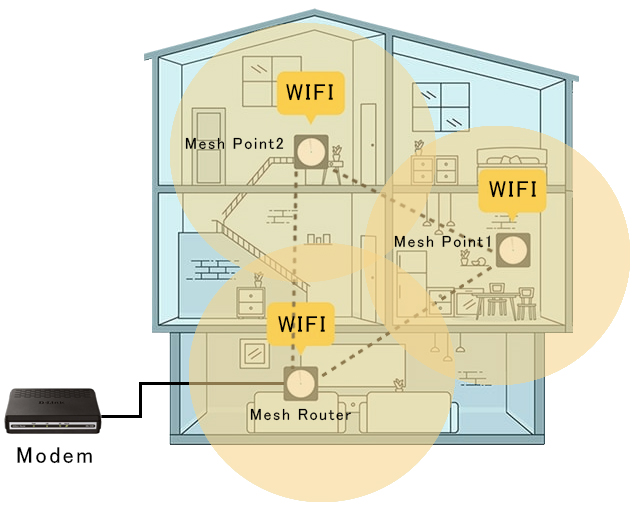
Mesh WiFi is a revolutionary technology that eliminates WiFi dead zones and provides consistent coverage throughout your home or office. It works by using a network of interconnected nodes, instead of a single router, to extend the signal and provide seamless roaming. This means that you can move from room to room without having to worry about losing your connection.
What is Mesh WiFi
Mesh Wi-Fi uses sophisticated algorithms and smart routing protocols to ensure seamless communication between the nodes. These protocols constantly monitor the network, identifying the best routes for data transmission. This dynamic routing ensures that data packets take the most efficient path through the network, optimizing your internet speed and minimizing latency.
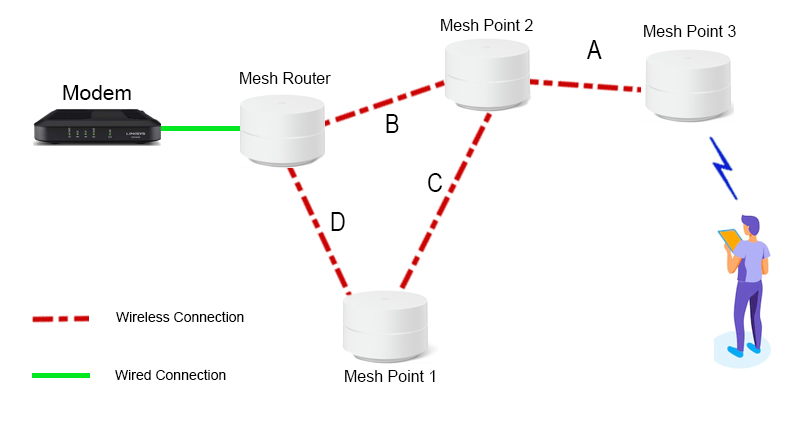
In a mesh WiFi network, each node acts as a standalone router, working together with other nodes to create a unified network. Unlike traditional WiFi networks, where all devices connect directly to the router, mesh WiFi devices connect to the closest node. This allows for a more efficient and reliable network, as the signal is not dependent on a single point of failure.
Mesh WiFi networks consist of two types of nodes:
- Mesh Router(Router Node): The router node is the central hub of the network and is connected to your internet modem. It provides the main WiFi signal for your home.
- Mesh Point (Satellite Node): Satellite nodes are smaller devices that are placed throughout your home to extend the WiFi signal. They communicate with each other and with the router node to create a single, seamless network.
Experience Seamless WiFi connection with Mesh Network
Types of Mesh Networks
When we talk about mesh WiFi, we’re really talking about how your routers connect and communicate with each other, and how they serve your devices. There are different ways mesh systems handle this, and understanding these methods is crucial to finding the best setup for your home. Let’s start to explain each mode: Dedicated Backhaul, Wireless Backhaul, and Wired Backhaul.
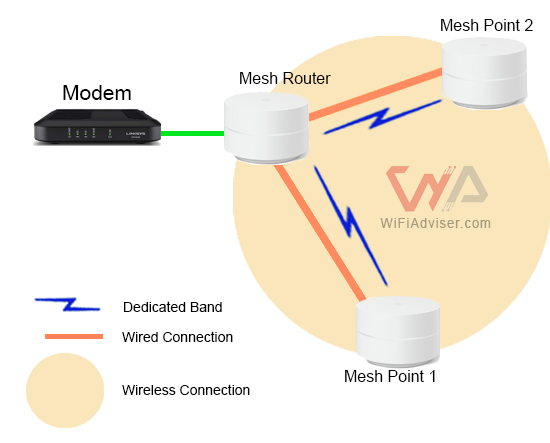
1- The “Express Lane” Mesh: Dedicated Backhaul
Imagine a highway with a special lane just for the mesh network itself. That’s dedicated backhaul. These systems have a separate Wi-Fi band specifically for communication between mesh routers, allowing the other bands to provide Wi-Fi service to network clients. This means faster speeds and less congestion, especially when you have a lot of devices connected. Here’s how it often works:
- Dual-Band Routers: If you have a dual-band mesh system (meaning it uses both 2.4GHz and 5GHz), the 5GHz band is often dedicated to the mesh backhaul – the communication between the nodes. This leaves the 2.4GHz band for your phones, laptops, and other devices. Think of it as the 5GHz being the express lane for the mesh, and the 2.4GHz being the regular traffic lanes for your devices.
- Tri-Band Routers: With a tri-band system (2.4GHz, 5GHz, and another 5GHz), one of the 5GHz bands is usually dedicated to the mesh backhaul. This allows the 2.4GHz and the remaining 5GHz band to serve your clients and devices, providing even more bandwidth and less congestion. This setup is like having a dedicated high speed lane for the mesh network.
2- The “Shared Road” Mesh: Wireless Backhaul
Now, let’s talk about the most common type of mesh: Wireless Backhaul. In this setup, there’s no dedicated lane. Instead, everyone shares the same road. This means the same Wi-Fi bands are used for communication between mesh routers and also for providing Wi-Fi service to clients. It’s like a busy street where everyone needs to share the space.Here’s how it works:
- Single-Band: Some routers use just the 2.4GHz band. This means both the communication between mesh routers and the Wi-Fi service to client devices happen on the same frequency.
- Dual-Band: Most often, you’ll see dual-band systems (2.4GHz and 5GHz). Both bands can be used for the mesh network and to provide Wi-Fi service to network clients. This means the mesh routers and your phones, laptops, and other devices are all communicating on the same frequencies.
3- Wired Backhaul Mesh: The “Super Highway”
For the absolute fastest and most reliable mesh, you can go wired. In this setup, the mesh routers connect to each other using Ethernet cables, specifically RJ45 cables. This creates a super-fast, stable connection between the routers, freeing up all the Wi-Fi bands for your devices. Here’s how it works:
- RJ45 Connection: Each mesh router is connected to another using an RJ45 Ethernet cable. This wired connection provides the backhaul, or the communication pathway between the routers.
- Dedicated Client Bands: Because the routers communicate via wires, all the Wi-Fi bands (2.4GHz, 5GHz, and any additional bands) are available to provide Wi-Fi service to client devices.
Mesh WiFi Types: How Dedicated, Wireless, and Wired Backhaul Work.
In Summary: Choosing the Right Mesh for You
Each mesh WiFi type offers unique advantages, catering to different needs and budgets. Whether you prioritize speed, affordability, or ease of setup, understanding the differences between Dedicated, Wireless, and Wired Backhaul can help you make an informed decision and build the perfect network for your home. We’ve summarized the pros and cons of each type in the table below.
| Mesh Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Backhaul |
|
|
| Wireless Backhaul |
|
|
| Wired Backhaul |
|
|
How to Setup Mesh Network?
Setting up a mesh WiFi network is different in each brand also more straightforward than you might think. Most mesh WiFi systems come with a mobile app that guides you through the installation process. You simply connect the first node to your existing modem or router and place it in a central location. Then, you add additional nodes in areas where you need better coverage. The nodes communicate with each other wirelessly, creating a seamless network.
Mesh WiFi also offers a range of additional features that enhance your overall internet experience. Many systems come with advanced security features such as built-in firewalls, encryption, and parental controls. Some systems also offer mesh network prioritization, where certain devices can be given higher priority for bandwidth. This is especially useful in homes or offices where multiple users are streaming videos or playing online games.
For More Information About Setup Mesh Routers:
Benefits of Mesh WiFi
One of the key benefits of mesh WiFi is its ability to provide extended coverage. With traditional WiFi networks, the signal strength drops significantly the further away you are from the router. But with mesh WiFi, each node acts as a signal relay, allowing the network to reach areas that were previously unreachable. This makes it ideal for larger homes or buildings with multiple floors.
In addition to extended coverage, mesh WiFi also offers better performance. Traditional WiFi networks can suffer from congestion and interference, especially in densely populated areas. Mesh WiFi uses smart algorithms to dynamically route traffic, ensuring that devices are always connected to the node with the best signal strength. This helps minimize latency and keeps your connection stable and fast. Mesh WiFi offers several benefits over traditional WiFi routers, including:
- Wider Coverage: Mesh WiFi networks provide consistent coverage throughout your home, eliminating dead zones and providing reliable connections in even the most remote areas.
- Seamless Roaming: With mesh WiFi, you can move from room to room without having to worry about losing your connection. Your devices will automatically switch between nodes as you move, ensuring a seamless internet experience.
- Improved Speed: Mesh WiFi networks can improve the speed of your WiFi connection by offloading traffic from the router node to the satellite nodes. This can be especially beneficial for homes with multiple devices and high internet usage.
- Simplified Management: Mesh WiFi networks are typically easier to manage than traditional WiFi routers. They often come with a smartphone app that allows you to easily set up, monitor, and troubleshoot your network.
Mesh Network Diagram Overview
Choosing a Mesh WiFi System
There are many different mesh WiFi systems available on the market, so it can be difficult to know which one is right for you. Here are a few things to consider when making your decision:
- Size of your home: If you have a large home, you will need a system with more nodes to provide consistent coverage throughout the entire house.
- Number of devices: If you have a lot of devices that connect to the internet, you will need a system with a high capacity to handle the traffic.
- Budget: Mesh WiFi systems range in price from around $100 to $1000 or more. Consider your budget and choose a system that fits your needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mesh WiFi is a revolutionary technology that provides reliable and widespread coverage, better performance, and easy setup. Its ability to extend coverage and optimize network traffic makes it a great choice for homes or offices with multiple devices or areas with poor signal strength. With its range of additional features, mesh WiFi is an all-in-one solution that can enhance your internet experience. So, if you’re tired of weak WiFi signals and dead spots, it’s time to consider upgrading to mesh WiFi.





