What is WiFi Roaming?
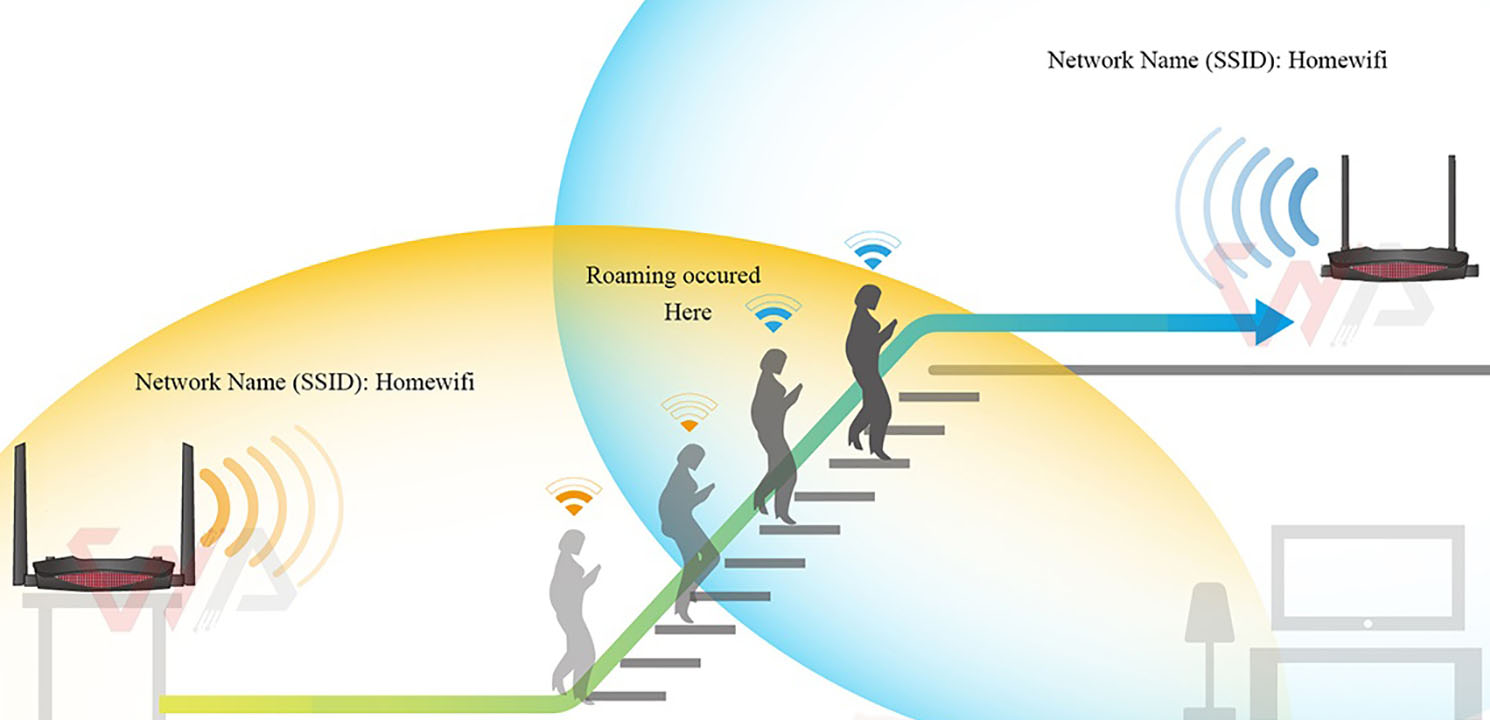
WiFi Roaming occurs when a smartphone , tablet or other wireless client device moves outside the usable range of a WiFi router and connects to another WiFi router. Roaming can also happen when the quality or strength of the client’s received signal drops. The client device automatically roams from one router to another as needed to provide seamless connectivity. Read this blog post to find more technical information about what is wifi roaming and how does it work.
WiFi roaming refers to the ability of devices to automatically connect to another WiFi router (same networks name) without any user intervention. This allows users to maintain a continuous internet connection as they move from one area to another, ensuring they don’t lose access to their online activities.
Wi-Fi Roaming: Staying Connected on the Move
Overall, WiFi roaming has become an essential feature for many modern users, allowing for greater flexibility and ease of access when it comes to staying connected to the internet while on the go.
How Does WiFi Roaming Work
Table of Contents
Toggle
First thing first , roaming is a client decision. The wireless client itself is responsible for detecting the need for roaming. In short, when the quality and strength of the received signal of the wireless client falls below a certain limit, it looks for a stronger router for connection. WiFi standards bodies (IEEE802.11/WiFi Alliance) do not specify when and how a client should roam.
It relies on a technology called Handover, which enables devices to detect and connect to nearby WiFi networks without any manual input. Handover mechanisms typically utilize protocols like Fast BSS Transition (FT) and Fast Dormancy to facilitate seamless transitions.
Read More: How to Access Your Router’s Settings
How to Improve Roaming Process ?
You may have experienced when you are walking between your WiFi Routers (they have the same wireless name and password), the wireless client (smart phone, tablet) is still sticking to the further router and will not roam (Move) to the near router. In order to overcome this problem, we introduce a practical way to improve the roaming process for android and windows clients.
1- For Windows Clients: Roaming Aggressiveness
Go to control panel -> network and internet -> network connection and choose the wireless connection from the network connections page. Right click the wireless connection and choose properties.

Select WiFi Network Connection
Click configure and you will see the following picture on the bottom. Choose Advanced and choose Roaming aggressiveness or Roaming sensitivity (based on your wireless network adapter brand).
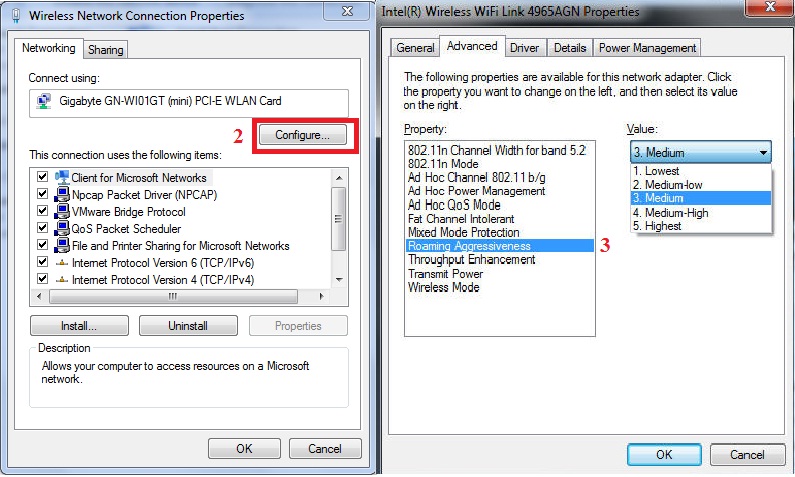
Auto-connecting: Wi-Fi Roaming Simplifies Network Access- Windows Settings
Now , you can control the Wireless client device roaming behavior by choosing the proper item from right menu. As you can see below, there are items from lowest to highest sensitivity:
- Lowest: Your wireless client will roam when link quality degrade significantly.
- Medium-Low/Medium-High: these are normal roaming sensitivities, when your signal quality degrades around 50% the clients tries to roam to another route or AP.
- Medium: Balanced setting between not roaming and performance.
- Highest: Your Wi-Fi client continuously tracks the link quality. If any degradation occurs, it tries to find and roam to a better router or AP.
2- For Android Clients: Wifi roaming fix
Unfortunately, there is no any specified configuration to control the smart phone roaming behavior, but you can use third party App’s for this purpose. for example, wifi roaming fix. you can simply set roaming sensitivity by changing the “Signal level” , -45 is a high , -65 is medium and -75 is low sensitivity levels.
Download From Google Play
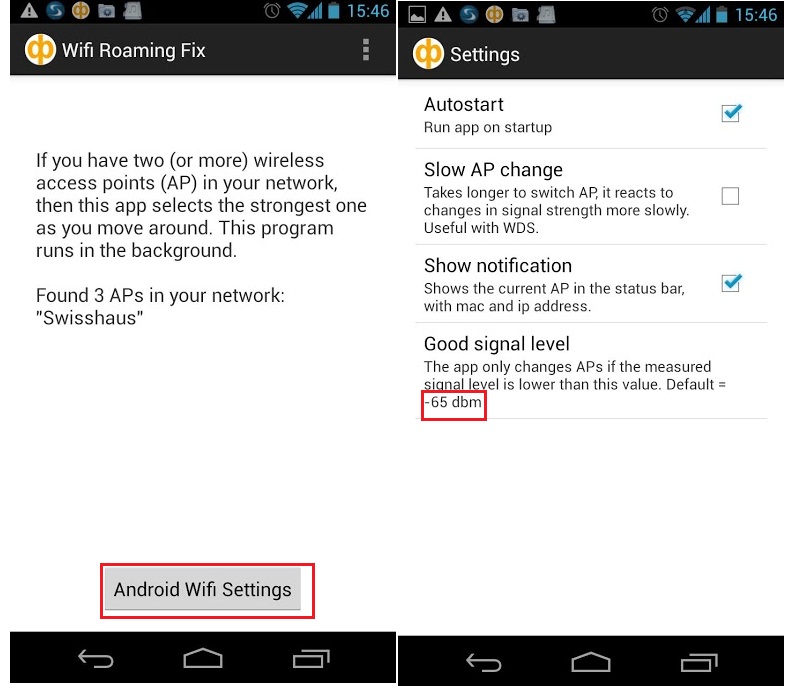
Auto-connecting: Wi-Fi Roaming Fix App
Conclusion
WiFi roaming is an essential feature that enhances the user experience and ensures continuous connectivity in today’s mobile world. By understanding the capabilities and benefits of WiFi roaming, we can optimize our network infrastructure and devices to provide a seamless and uninterrupted online experience.


