How to Choose Office WiFi Router
In today’s increasingly digital world, having a reliable and high-speed WiFi connection is essential for businesses of all sizes. A good WiFi router can provide stable connectivity for your employees, allowing them to access the internet, share files, and collaborate seamlessly. However, with so many different routers on the market, it can be difficult to know which one is right for your business.
Difference Between Home and Office WiFi Routers
office WiFi routers are designed with the needs of a larger scale and more demanding environment in mind, providing increased coverage, security, management capabilities, and reliability compared to home WiFi routers.
Since most office users use portable devices like laptop, smart phones, tablets, the existence of a highly stable wireless network is more important than a wired network. They also need high-speed connection to the wired network servers.
- Performance and Bandwidth
Offices often host numerous devices simultaneously, demanding high-performance routers capable of handling heavy data traffic and maintaining a stable connection amidst multiple users. Home routers, on the other hand, typically cater to a smaller number of devices, making moderate performance sufficient.
- Range and Coverage
Offices often occupy larger spaces, requiring routers with extended range to ensure consistent connectivity across various areas. Home routers, designed for smaller living spaces, may suffice with a shorter range.
- Security
Offices handle sensitive information, making it crucial to prioritize robust security measures. High-end office routers often include advanced security features like WPA3 encryption, firewall protection, and intrusion detection, safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access. Home routers, while still employing security protocols, may not be as heavily fortified due to the lower risk of data breaches.
- Features
Office routers often incorporate additional features catering to business needs, such as Quality of Service (QoS) prioritization, which ensures critical applications receive preferential bandwidth, and guest network capabilities for secure access by visitors or contractors. Home routers may prioritize features like parental controls and media streaming optimizations.
- Cost and Flexibility
Office routers, with their advanced features and higher performance demands, tend to be more expensive than home routers. Businesses may consider investing in a high-performance router to ensure uninterrupted operations and prevent network slowdowns. Home routers, often more affordable, provide basic connectivity for everyday tasks.
Consider the following Factors When Choosing an Office WiFi Router
Here are some tips on how to choose the best office WiFi router:
Number of users
The number of employees who will be using the WiFi network will affect the router’s performance. If you have a small office with a few employees, a basic router may be sufficient. However, if you have a larger office with many employees, you will need a router with more bandwidth and range.
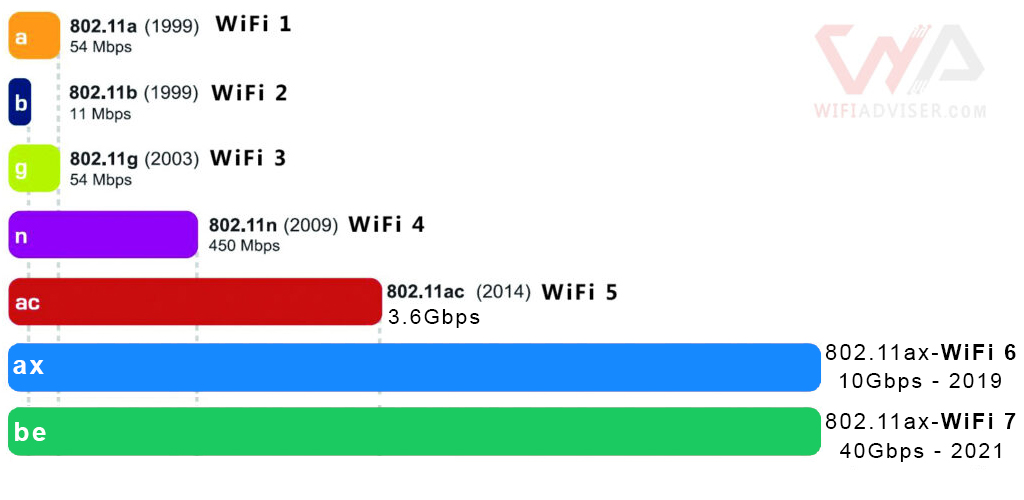
Wireless standard
WiFi routers use different wireless standards, such as 802.11n and 802.11ax. The newer standards are faster and more efficient, so they are a good choice for businesses with high bandwidth requirements.
Range
The range of the router is the area in which it can provide reliable connectivity. If you have a large office, you will need a router with a long range.
Dual-band or tri-band router
Dual-band routers offer both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands, which can provide more flexibility and options for connecting devices. Tri-band routers have an additional 5GHz band, which can help manage heavy network traffic more efficiently.
The Number Of Router’s Antenna
Technically, the number of antennas on the wifi router has a tremendous impact on the quality of client’s communication. Enables the router (especially the 802.11ac and 802.11ax routers) to use its own capabilities such as Beam-forming and MU-MIMO.
- Beamforming focus the router’s signal and sending it directly to the client, as a result minimizing the surrounding interferences and increasing the signal strength. Read More : What is Beamforming ?
- MU-MIMO allows multiple WiFi devices to simultaneously receive multiple data streams.
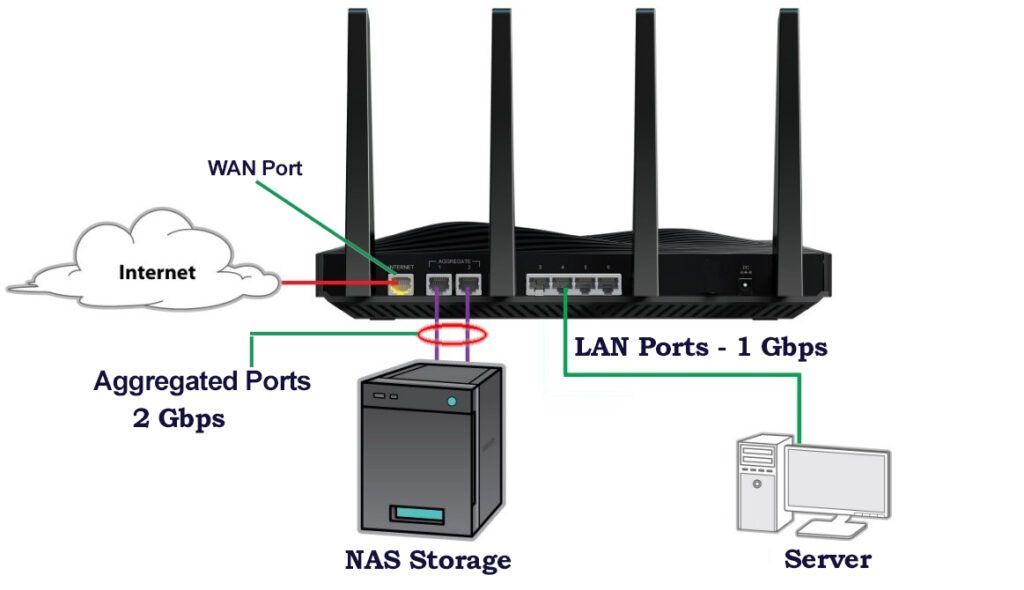
The Number of LAN/WAN Ports
Consider the number of wired devices you have in your office that require a direct connection to the router. Ensure that the router has enough Ethernet ports to accommodate these devices. Generally, most wifi routers are equipped with up to 4 ports to communicate with the wired network and servers, along with one WAN port for the Internet communication. The speed of most router’s LAN ports is 1Gbps.
New routers, equipped with a Multi-Gig LAN/WAN port. The speed of this port is 2.5Gbps. Keep in mind that to benefit from this speed , you should connect this port to a Multi-Gig compliant port.
Read More : Routers Equipped with Multi-Gig Ports.
Some routers have two specific ports with the Link Aggregation capability. These two ports are integrated as one logical port and made a 2Gbps LAN port, for serving the high-bandwidth required servers like file servers, storages, data-base servers. All business wifi routers should support this capability.
Powerful Port Connectivity: A Symphony of Data Flow
Routers with USB ports offer additional flexibility for connecting external devices and expanding network capabilities. These USB ports can be used for various purposes, including:
- File and Media Sharing
- Printing Wirelessly
- USB Device as a Server
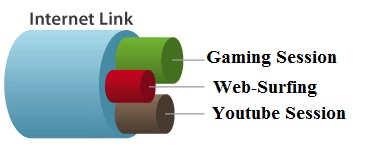
QOS and traffic-Shaping Features
Advance wifi routers have specific capabilities to manage the services and users bandwidth separately.
- QoS allows you to prioritize certain types of internet traffic, such as video conferencing or voice calls, over others to ensure smooth and uninterrupted performance.
- The Traffic-Shaping capabilities you can assign a certain amount of bandwidth to one or a group of users.
- For example, you can assign 5Mbps bandwidth for each client or 20Mbps bandwidth for a group of clients. You can assign these limitation to clients’ devices based on the their IP or MAC addresses.
Enhancing Network Performance: A QoS Guide to Priority Flow
Adjustable Output (Transmit) Power
In advanced office routers, you are able to set the router’s output power(TX Power) between 17 and 25dbm ( the wireless output power is measured in dbm) depending on the extent of the workplace and the existing obstacles and walls.
This value should be adjusted carefully so that all users have a RSSI around -65dbm. (RSSI means the received signal level at a certain point. This number can be between -30dbm and -85dbm. You can measure the RSSI at a certain location by WiFi Analyzer free apps) .
Keep in mind that increasing the router’s output power may cause users to lose quality in communication. So, try to choose the right amount for this option and avoid unnecessarily increasing it.
Brand Reputation and Customer Support
Choose a reputable brand that offers good customer support. This will ensure that you can receive assistance if you encounter any technical issues or require future upgrades.
Conclusion
The decision between a home and office Wi-Fi router hinges on your specific needs and budget. For small home offices with limited bandwidth demands, a standard home router may suffice. However, for larger offices with multiple users, high-traffic activities, and sensitive data, an advanced office router is essential.
By understanding the key differences between home and office Wi-Fi routers, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your workspace requirements. Whether you’re fostering productivity in an office or enjoying seamless connectivity at home, the right router will pave the way for a stable, secure, and high-performance Wi-Fi experience.





