What is Port Forwarding?
Port forwarding is a technique of forwarding traffic from one internet connection to internal network. This is useful when you have a device or service that needs to be accessed remotely, but it is hidden behind a network’s firewall. In simple terms, it is like creating a pathway to allow outside traffic to reach the device.
Port forwarding aids in simplifying remote access, online gaming, and hosting services. However, it is essential to note that opening ports can leave your device vulnerable to malicious activities. Therefore, it is recommended to use it with caution and configure appropriate security measures such as firewalls and password protection.
Why You Need Port Forwarding
This networking technique allows specific devices or services on your private network to receive incoming data from the internet. Without port forwarding, these devices would remain hidden behind your router’s firewall, unable to engage in external communication.Port forwarding is crucial for various applications, including:
Gaming: Games often rely on port forwarding to establish connections with remote servers, enabling online multiplayer experiences.
Remote Access: Port forwarding facilitates remote access to devices on your local network, such as shared media servers or home automation systems.
Home Security Systems: Home security cameras and other devices often require port forwarding to communicate with the cloud for remote monitoring and alerts.
Web Servers: If you have a personal web server running on your home network, port forwarding will allow visitors to access it from the internet.
How Does Port Forwarding Work?
Imagine your home network as a private city, with your router serving as the city gates. Incoming data from the internet is like visitors approaching the gates, seeking entry into your network. By default, the gates are closed, blocking all incoming traffic. Port forwarding acts as a special key that grants specific visitors, identified by port numbers, access to specific devices or services within your network.
In the simplified example below, a remote computer (81.16.22.43) sends a request to 2.3.4.5 on port 801 (which is defined and mapped to port 8010 for 192.168.1.1, in the router’s forwarding table).
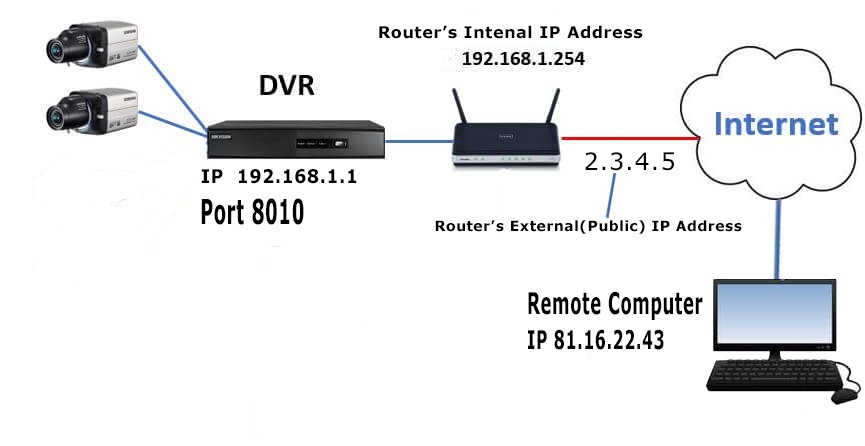
How Does Port Forwarding Work?
Stage 1:
When data originating from the internet arrives at your router, it enters the router’s firewall, which acts as a gatekeeper. By default, the firewall blocks all incoming traffic, ensuring that only authorized devices can access your network.
Stage 2:
The firewall examines the incoming data packet, specifically the destination port number. The port number serves as a unique identifier for specific applications or services within the network. If the port number matches a port forwarding rule configured on the router, the firewall recognizes it as a legitimate request for access.
Stage 3:
Upon detecting a matching port forwarding rule, the firewall directs the incoming data packet to the specified device or service on the local network. The router acts as a relay, forwarding the data to the authorized device based on the port number and IP address specified in the forwarding rule.
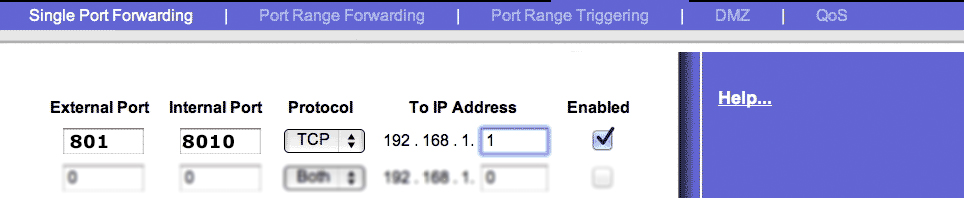
Port Forwarding Configuration Page
Read More :What is Dynamic DNS ( DDNS )
Conclusion
Port forwarding is a powerful tool that can unlock the full potential of your home network. By carefully configuring port forwarding rules, you can enable remote access, online gaming, and other advanced features, enhancing your internet experience. However, it’s essential to prioritize security by opening ports only for authorized applications and services. With proper planning and caution, port forwarding can transform your home network into a versatile and secure platform for accessing the world online.