If you are installing a Wi-Fi network, it is important that one of the first things you do understand what sorts of different Wi-Fi standards exist. Based on these standards, ranges of speed and distance can be charted between components which may impact the reliability. If you are looking for a more technical information, please read the following blog about Wifi Standards Chart. Understanding the most recent advancements and how they affect our connectivity is not as simple we would expect, especially when new WiFi standards are released. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive guide to standards, covering everything from their history and specifications to their practical applications.
WiFi Standards Overview
Today, WiFi Router has become an essential unit for all home and business owners in finding a reliable network. However as this technology rapidly grows, they experience many WiFi standards from its alphabet soup of acronyms. You should be familiar with wifi standards specifications, they all basically mean a few things:
- How far can the wireless signal reach
- How much data can the signal send
- Is it backwards compatible with other standards
To make it easier to understand, Just think how far can a wireless signal go, and how fast can it transmit data. Now the standards will make more sense. Wifi standards rapidly changed every few years to bring faster internet, better connections and more simultaneous users.
What is “WiFi” and “IEEE 802.11” ?
WiFi, which stands for Wireless Fidelity, has evolved through a series of standards, each introducing significant improvements in speed, range, and efficiency. WiFi is a specific trademark owned by the Wi-Fi Alliance, a group dedicated to certifying that WiFi products meet the IEEE 802.11 wireless standards.
✅ They are not the same thing, despite their close relationship. To put it another way, 802.11 is the technical recipe or blueprint that describes how devices connect wirelessly. Conversely, the 802.11 standard-compliant goods and services are branded under the moniker Wi-Fi. To put it another way, Wi-Fi is the “how” while 802.11 is the “what”.
WiFi Standards Specifications
Speed and Frequency are two fundamental changes in WiFi standards:
- Speed means How much data the wireless network can transmit.
- Frequency means what radio frequency the data is carried on. These are either 2.4Ghz , 5 Ghz and 6Ghz.
Read More: How to Extend WiFi Range
Here’s a WiFi standards chart (Table) of each 802.11 standards type based on its designation:
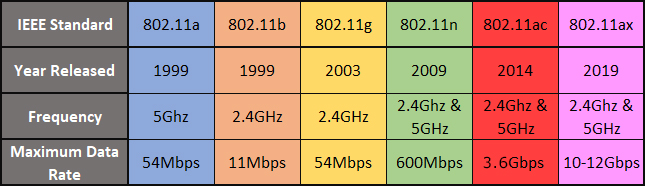
WiFi Standards Overview
802.11a (Wi-Fi 2)
One of the older Wi-Fi standards, 802.11b has a maximum speed of 54 Mbps and a range of about 150 feet. This standard is rarely used today.
802.11b (Wi-Fi 1)
One of the older Wi-Fi standards, 802.11b has a maximum speed of 11 Mbps and a range of about 150 feet. This standard is rarely used today.
802.11g (Wi-Fi 3)
A popular Wi-Fi standard in the mid-2000s, 802.11g has a maximum speed of 54 Mbps and a range of about 150 feet. This standard is still used today, but is being phased out in favor of newer standards.
802.11n (Wi-Fi 4)
A newer Wi-Fi standard that debuted in 2009, 802.11n has a maximum speed of 600 Mbps and a range of about 300 feet. This standard is still common today, but is being replaced by even newer standards.
802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5)
The current Wi-Fi standard for high-speed connections, 802.11ac has a maximum speed of 1 Gbps and a range of about 300 feet. This standard is ideal for streaming video or other bandwidth-intensive tasks.
802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6)
The upcoming Wi-Fi standard for even faster connections, 802.11ax promises to deliver speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This standard is still in development and is not yet widely available.
Wi-Fi 6E
From April 2020, the WiFi 6E standard was officially introduced and the 6Ghz frequency was added to the allowed frequencies of WiFi networks.
802.11be (Wi-Fi 7)
The future Wi-Fi standard, 802.11be, known as Wi-Fi 7, is set to achieve speeds up to 46 Gbps with enhanced performance and reduced latency, using frequencies 6GHz, 5GHz, and 2.4GHz, supporting next-gen applications like VR and AR.
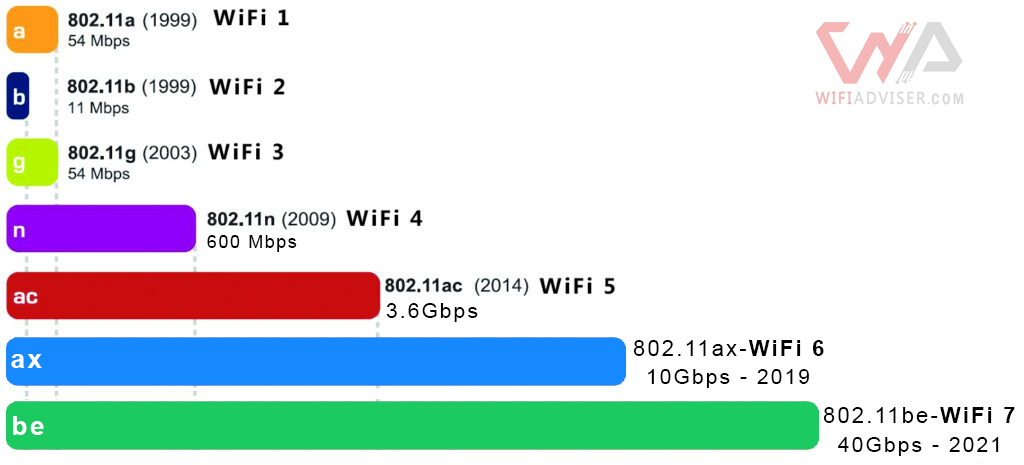
WiFi Standards Chart-2025
WiFi Standards Compatibilities
Standards compatibility considerations in WiFi Routers:
- 802.11be WiFi 7 Router is a Tri-band router(2.4Ghz ,5Ghz , 6Ghz bands) and can communicate with 802.11b/g/n/ac/ax and 6Ghz-compatible clients.
- 802.11ax WiFi 6E Router is a Dual-band or Tri-band router(2.4Ghz
,5Ghz , 6Ghz bands) and can communicate with 802.11b/g/n/ac/ax and 6Ghz-compatible clients. - 802.11ax WiFi 6 Router is a Dual-band or Tri-band router(2.4Ghz ,5Ghz bands) and can communicate with 802.11b/g/n/ac/ax clients.
- 802.11ac WiFi Router is a Dual-Band or Tri-band router and can communicate with 802.11b/g/n/ac clients.
- 802.11n single band WiFi Router (2.4Ghz band) can communicate with 802.11b/g/n clients in 2.4Ghz frequency band.
- 802.11n dual band WiFi Router(2.4Ghz and 5Ghz bands) can communicate with 802.11 b/g/n clients in both 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz frequency bands.
- 802.11g WiFi Router(2.4Ghz band) can communicate with 802.11b/g devices.
- 802.11b WiFi Router(2.4Ghz band) can communicate with only 802.11b devices.
Read More: What is WiFi Channel and Channel Width
New WiFi Standards Naming Convention
Over time, different classifications of WiFi networks were given different naming conventions. All of them are using the same scheme for example:
- 802.11ac as a router’s communication generation.
- 802.11k as a router’s communication capability (for roaming issues in enterprise WiFi networks).
As you see , both using the same schema, and it can be a little confusing for users to understand and differentiate between them.
Recently , the WiFi standard has changed to a new classification, to help make it easier for consumers to understand. Instead of memorizing a dual-purposed alphabet combination, they can use a simple naming. As can see in the followint table , you can use “WiFi 5” instead of “802.11ac or “WiFi 6” instead of “802.11ax” .
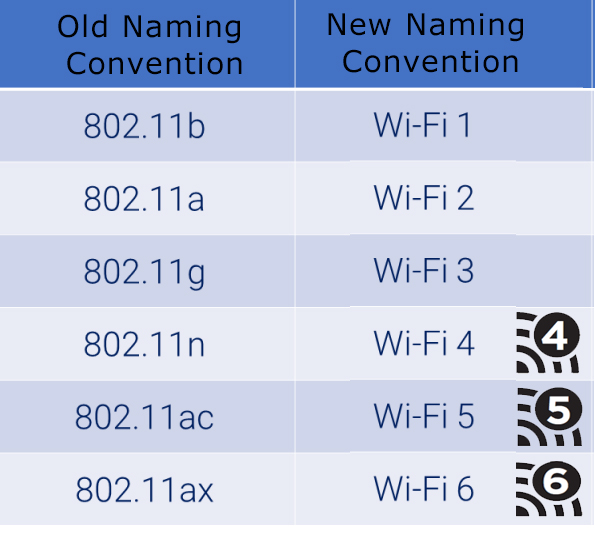
WiFi Standards Naming Convention
What is Wi-Fi 6 Technology?
Technically, WiFi 6 is the successor to the WiFi5 (802.11ac) standard and operates in the 2.4GHz and 5GHz spectrum. This standard enables WiFi Routers and Clients to send more data in one transmission stream, resulting in speed improvements of up to 20% to 40% with higher modulation rate (1024-QAM). Higher modulation increases the efficiency and speed of data transmission on your network.
The 2.4GHz Frequency is back
✅ The 2.4Ghz band is available in WiFi6 standard, while the industry has shifted to 5GHz WiFi for less interference. 2.4GHz is still better at penetrating solid objects. And there shouldn’t be as much interference for 2.4GHz as old wireless (non-WiFi but 2.4GHz) equipment like cordless telephones and wireless baby monitors are retired.The advantages of Wi-Fi 6 at a glance:
- Stable Wireless connections : Due to use of Beamforming technology.
- Less Latency : Using technologies such as OFDMA and MU-MIMO.
- Longer Battery Life: The client’s WiFi radio only turns on when needed.
- More Speed : Due to use of 1024-QAM modulation.
- More Security: By using the WPA3 security protocol.
What is Wi-Fi 6E Technology?
Wi-Fi 6E is a newly introduced technology for Wi-Fi devices that operates on the 6 GHz frequency band. Unlike the existing 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands, WiFi6E provides significantly wider channel bandwidths for faster data transmission rates. The 6 GHz frequency band offers up to seven 160 MHz channels, which is three times wider than the maximum channel width available in the 5 GHz band, resulting in better network performance and reduced congestion. Wi-Fi 6E has been designed to coexist with existing WiFi networks, devices, and technologies. Which ensures backward compatibility with other WiFi 6 devices while leveraging the newer 6 GHz frequency band. Read More…
What is Wi-Fi 7 Technology?
Wi-Fi 7 is set to offer even better capabilities, supporting 2.4GHz, 5GHz, and 6GHz, providing even faster speeds than Wi-Fi 6E. Moreover, this technology comes with much more advanced features such as multiple channels in both uplink and down-link directions. It introduces 320MHz channel width, doubling the maximum of WiFi 6E, enabling data transfer speeds of up to 46 Gbps. Additionally, WiFi 7 utilizes a new frame format called Multi-Link Operation (MLO), which simultaneously utilizes multiple antennas to further boost performance. Read More…
Conclusion
WiFi standards have played a pivotal role in shaping the way we connect to the internet. By understanding the history and specifications of these standards, we can better appreciate their impact on our daily lives and anticipate the advancements that lie ahead. As WiFi technology continues to advance, we can look forward to even more seamless and efficient wireless connectivity, enabling us to embrace the possibilities of a truly connected future.





